Have you experienced specific problems when trying to use an exception to preserve and archive specific works or other subject matter in your collection?
Comments closedCategory: EU
Criminal enforcement measures
In addition to civil enforcement measures harmonised by the Enforcement Directive and the Information Society Directive, EU Member States also apply criminal procedure and penalties to ensure enforcement of intellectual property rights, in line with Article 61 of the TRIPS Agreement.
Comments closed
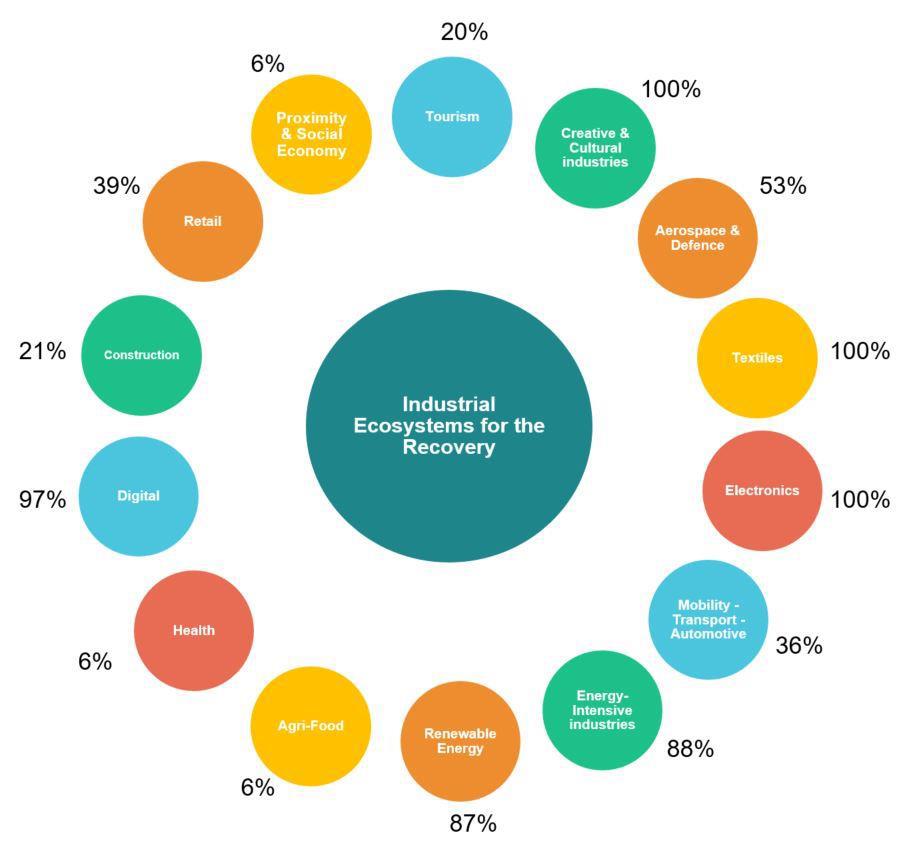
The challenge ahead: capitalizing on Europe’s intellectual assets to boost recovery and resilience
Intangible assets such as inventions, artistic and cultural creations, brands, software, knowhow, business processes and data are the cornerstones of today’s economy. Over the last two decades, the volume of annual investments in such ‘intellectual property products’ increased by 87% in the EU, while the volume of tangible (non-residential) investments increased by only 30%. Investments in intangibles were also significantly less affected by the 2008 economic crisis.
Comments closed
Online intermediary services and online search engines play a crucial role in enabling and promoting digital trade. In order to strengthen the trust of business users and consumers and encourage them to take part in the vast digital ecosystems created by online platforms, it is necessary to set minimum standards for their services.
Comments closed
Would it be necessary in your country to enact legislation to ensure that the results of the 2011 MoU (i.e. the agreements concluded between libraries and collecting societies) have a cross-border effect so that out of commerce works can be accessed across the EU?
Would it be necessary to develop mechanisms, beyond those already agreed for other types of content (e.g. for audio- or audio-visual collections, broadcasters’ archives)?
Comments closed
Irrespective of establishment of liability, EU law ensures that rights holders have the possibility to apply for an injunction against intermediaries whose services are used by third parties to infringe their Intellectual property rights (IPR).
Comments closed
The combined application of the preferred options would affect all types of stakeholders differently, but is not expected to result in any disproportionate impact on a specific category of stakeholders.
Comments closedKey points:
- Rights holders can avail of civil enforcement measures against both direct infringers and intermediaries.
- A wide spectrum of blocking injunctions can be sought against internet access providers to repress IPTV infringements.
- Internet intermediaries can receive orders to disclose information on infringers; however, disclosure of information on end-users of illegal IPTV services may not be compatible with EU data protection law.
- Criminal measures are also available in all EU Member States against IPTV infringers on a commercial scale.
- Import and sale of IPTV devices may be prohibited on the ground of non-compliance with EU standards on radio equipment.
Imposing transparency obligations on the contractual counterparty of creators supported by a contract adjustment right and a dispute resolution mechanism
I. Contract adjustment mechanism
This mechanism would improve the effectiveness of the reporting obligation under Option 2 since it would provide creators with legal means to request adjustment of the remuneration on the basis of the information received in reporting statements.
Comments closed
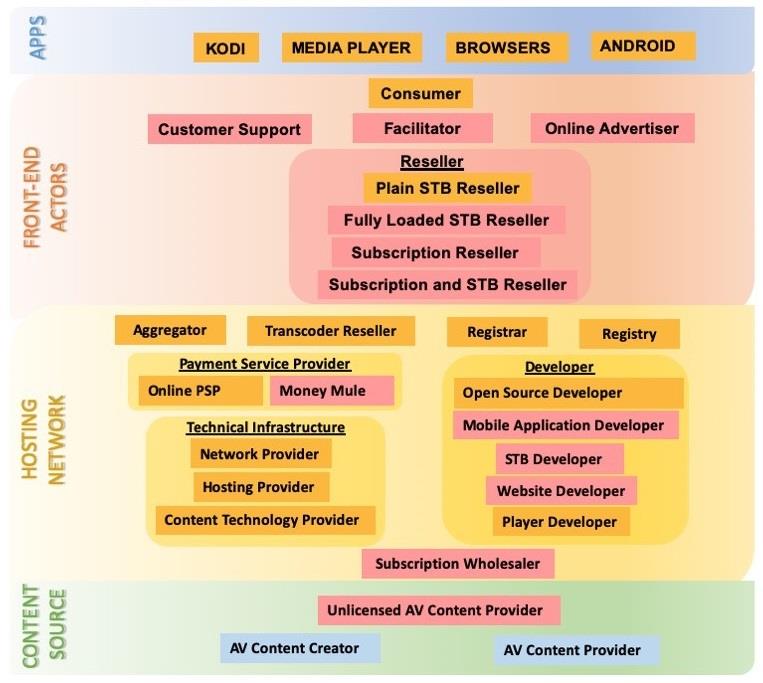 Another part of fundamental EU research on IPTV. Now – actors and ecosystems participants. The ecosystem for unauthorised IPTV includes several actors. They consist of primary infringers (the providers of the unauthorised content), a series of active and passive intermediaries, and final consumers. In addition, a number of facilitators and enablers can also be involved by giving instructions and providing tutorials for the installation of middleware — software instrumental for the fruition of the unauthorised content.
Another part of fundamental EU research on IPTV. Now – actors and ecosystems participants. The ecosystem for unauthorised IPTV includes several actors. They consist of primary infringers (the providers of the unauthorised content), a series of active and passive intermediaries, and final consumers. In addition, a number of facilitators and enablers can also be involved by giving instructions and providing tutorials for the installation of middleware — software instrumental for the fruition of the unauthorised content.
Comments closed